Varicose veins are enlarged, swollen, and twisted veins that often appear blue or dark purple. They are typically found in the legs and feet due to the increased pressure in these areas from standing and walking. Varicose veins are caused by weak or damaged valves in the veins, which prevent blood from flowing properly. As blood pools in the veins, they enlarge and become visible through the skin. In this article we will look at varicose veins causes, symptoms, and treatments.
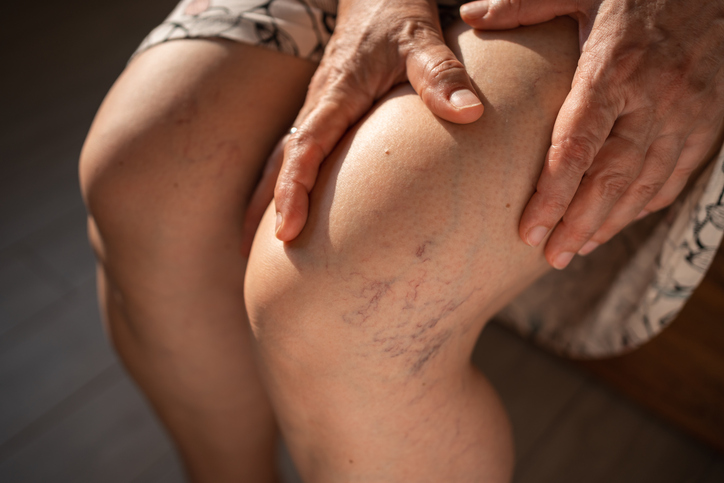
Common Causes for Varicose Veins
Common symptoms of varicose veins include aching, swelling, and a feeling of heaviness in the legs. In more severe cases, varicose veins can lead to pain after sitting or standing for long periods, throbbing, or cramping in the legs. Skin discoloration or ulcers near the ankles may also occur. While varicose veins are often a cosmetic concern, they can indicate underlying vascular issues that may require treatment.
Non-Surgical Treatments for Varicose Veins
Many people seek treatment for varicose veins to relieve symptoms and improve the appearance of their legs. Non-surgical treatments are usually the first option for those with mild to moderate varicose veins, and these methods can be highly effective in reducing discomfort and improving the look of affected veins.
One common non-surgical treatment is compression stockings, which help improve blood flow by applying pressure to the legs. These stockings reduce swelling and prevent blood from pooling in the veins. While compression stockings don’t eliminate varicose veins, they can significantly ease symptoms.
Sclerotherapy is another popular non-surgical option. This procedure involves injecting a solution directly into the varicose vein, causing it to collapse and eventually fade away. Sclerotherapy is effective for smaller varicose veins and spider veins, and patients often see noticeable results after just a few sessions.
Endovenous laser treatment (EVLT) is a minimally invasive procedure where a laser is used to heat and close the affected vein. This treatment is performed under local anesthesia, and patients can typically return to their normal activities the same day. EVLT is ideal for treating larger varicose veins and has a high success rate.
Surgical Options for Severe Varicose Veins
For individuals with more severe or persistent varicose veins, surgery may be necessary. Surgical treatments are generally recommended when non-surgical options fail or when varicose veins lead to serious complications such as leg ulcers, bleeding, or deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
One surgical option is vein stripping, a procedure where the affected vein is removed through small incisions. This surgery is often performed under general anesthesia and may require a longer recovery period compared to non-invasive treatments. Vein stripping is highly effective at removing large varicose veins and preventing their recurrence.
Another surgical treatment is ambulatory phlebectomy, which involves the removal of smaller varicose veins through tiny punctures in the skin. This procedure is typically performed under local anesthesia, and patients can often return to normal activities within a few days. Ambulatory phlebectomy is an effective option for treating superficial veins that are causing discomfort or cosmetic concerns.
For those with severe venous insufficiency, endoscopic vein surgery may be required. This procedure involves inserting a tiny camera into the vein to visualize and remove the damaged sections. Endoscopic vein surgery is usually reserved for cases with complications such as leg ulcers.
Radiofrequency Ablation: A Modern Approach
Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is another minimally invasive treatment for varicose veins. This technique uses radiofrequency energy to heat and seal off the affected vein, causing blood to reroute to healthier veins. RFA is performed using local anesthesia, and patients typically experience little discomfort and minimal downtime after the procedure.
One of the key advantages of RFA is its high success rate in treating large varicose veins without the need for invasive surgery. The procedure is also known for its quick recovery time, with most patients able to resume normal activities within 24 hours.
Lifestyle Changes and Prevention
While treatments are effective in addressing varicose veins, certain lifestyle changes can help prevent their occurrence or minimize symptoms. Maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and avoiding prolonged periods of standing or sitting are all essential in promoting healthy circulation and reducing the risk of varicose veins.
Elevating your legs when resting, wearing compression stockings, and avoiding high heels are also helpful measures. These small adjustments can make a significant difference in managing the discomfort associated with varicose veins and preventing new ones from forming.
Risks and Considerations
As with any medical treatment, it’s important to weigh the risks and benefits before undergoing varicose vein procedures. While non-invasive treatments like sclerotherapy and EVLT are generally low-risk, side effects such as bruising, swelling, and mild pain may occur. Surgical treatments carry additional risks such as infection, blood clots, and scarring, so it’s essential to discuss all options with a healthcare provider.
For those with underlying venous conditions, varicose veins may recur even after treatment. Regular follow-up appointments and lifestyle changes are critical in managing long-term vascular health.
Conclusion
Varicose veins can cause discomfort, swelling, and aesthetic concerns, but a variety of effective treatments are available to address these issues. From non-surgical options like sclerotherapy and compression stockings to more advanced procedures like endovenous laser treatment and radiofrequency ablation, there are solutions for every severity of varicose veins. By consulting with a healthcare provider, individuals can find the best treatment plan and take steps to prevent future complications.


